Study Material
Number System:
The number system is a fundamental concept in mathematics and forms the basis for various calculations and problem-solving techniques. Mastering the number system is crucial for excelling in competitive exams, as it helps improve accuracy and speed. In this study guide, we will explore important concepts, tips, and tricks related to the number system that will aid you in your exam preparation.
Classification of Numbers:
Numbers can be classified into various categories based on their properties and characteristics. Let's explore the main classifications of numbers:
A. Natural Numbers (N): Natural numbers are the set of positive integers, starting from 1 and extending infinitely. They are used for counting and do not include zero or negative numbers.
Example: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ...
B. Whole Numbers (W): Whole numbers include all the natural numbers along with zero. They form the set of non-negative integers.
Example: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, ...
C. Integers (Z): Integers encompass both positive and negative whole numbers, along with zero.
Example: ..., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ...
D. Rational Numbers (Q): Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as a fraction of two integers. They can be terminating or repeating decimals.
Example: 1/2, -3/5, 0.75, 2.333..., ...
E. Irrational Numbers (I): Irrational numbers cannot be expressed as a fraction and have non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansions. They are typically represented using radical symbols.
Example: √2, π (pi), e (Euler's number), ...
F. Real Numbers (R): Real numbers encompass both rational and irrational numbers, forming the set of all possible numbers on the number line.
Example: All rational and irrational numbers together.
Notable Properties of Number Systems: Each classification of numbers has its own unique properties:
A. Closure Property: The closure property states that the sum or product of two numbers from the same set will always belong to that set.
Example: The sum of two natural numbers is always a natural number (e.g., 3 + 5 = 8).
B. Commutative Property: The commutative property holds for addition and multiplication, stating that changing the order of numbers in an operation does not affect the result.
Example: 4 + 2 = 2 + 4 and 3 * 6 = 6 * 3.
C. Associative Property: The associative property holds for addition and multiplication, stating that the grouping of numbers in an operation does not affect the result.
Example: (2 + 3) + 4 = 2 + (3 + 4) and (5 * 6) * 2 = 5 * (6 * 2).
D. Distributive Property: The distributive property links addition and multiplication, stating that multiplying a number by a sum is the same as multiplying the number by each addend separately and then adding the results.
Example: 2 * (3 + 4) = (2 * 3) + (2 * 4).
Quantative Aptitude/Numerical Aptitude :
In this article, we will cover all sections which are crucial to prepare for any bank exam or any other exam also.
- Number System
- Decimal Fractions
- Indices & Surds
- Square Root & Cube Root
- HCF and LCM
- Simplification
- Average
- Ratio and Proportion
- Problem on Ages
- Percentage
- Profit and Loss
- Ratio & Proportion
- Partnership
- Orders of Magnitude
- Unitary Method
- Time and Work
- Time and Distance
- Alligation or Mixture
- Probability
- Simple & Compound Interest
- Area
- Pipes and Cisterns
- Problems on Trains
Please click on below link to get more Banking jobs 2023
Decimal Fractions Complete Tutorial
30-07-2023
What are Decimal Fractions?
Decimal fractions are numbers that include a decimal point, representing a part of a whole number.
They are also known as decimal numbers and are used to express quantities that are not whole numbers.
A number in the form of X/Y where Y 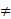 0 is known as fraction.
0 is known as fraction.
where X= Numerator and Y = Denominator.
Fraction = Numerator/Denominator
Example: 0.5, 1.25, 3.75, 8.9, etc.
Converting Decimal to Fraction: To convert a decimal fraction to a regular fraction,
follow these steps:
- Write the decimal as the numerator.
- Put the appropriate power of 10 as the denominator.
Example: Convert 0.75 to a fraction. 0.75 = 75/100 = 3/4
Converting Fraction to Decimal: To convert a fraction to a decimal, perform the division to get the decimal equivalent.
Example: Convert 5/8 to a decimal. 5 ÷ 8 = 0.625
Multiplying and Dividing Decimal Fractions:
a) Multiplication: Treat the decimals as whole numbers, ignoring the decimal point. Count the total number of decimal places in the given numbers and place the decimal point in the product accordingly.
Example: 1.5 * 2.4 = 3.6 (1 decimal place + 1 decimal place = 2 decimal places)
b) Division: Move the decimal point in the divisor and dividend to make the divisor a whole number. Then, divide as usual.
Example: 0.6 ÷ 0.2 = 3 (move decimal in 0.6 once to make it 6, and 6 ÷ 2 = 3)
Study Material for Bank Exams [ 2023 ]
06-07-2023
Free Study Material for Bank Exams like SBI, IBPS & All Other Competitive Exams
Study Material :
- Qunatitative Aptitude
- Reasoning
- Data Interpretation
- English
- Computer Knowledge
- Marketing Aptitude
- General Awareness/Current Affairs
- Group Discussions
- Previous Year Q/A
- 8500+ Fans
- 10000+ Subscribers
- 9000+ Subscribers
- 10000+ Followers
- 12000+ Followers
- 8000+ Followers
- All India Jobs
- Gujarat Jobs
- Bihar Jobs
- Maharastra Jobs
- All India Jobs
- Andhra Pradesh Jobs
- Assam Jobs
- Chhattisgarh Jobs
- Goa Jobs
- Haryana Jobs
- Jammu and Kashmir Jobs
- Karnataka Jobs
- Lakshadweep Jobs
- Meghalaya Jobs
- Nagaland Jobs
- Pondicherry Jobs
- Rajasthan Jobs
- Tamil Nadu Jobs
- Tripura Jobs
- Uttarakhand Jobs
- Andaman and Nikobar Jobs
- Arunachal Pradesh Jobs
- Delhi Jobs
- Himachal Pradesh Jobs
- Jharkhand Jobs
- Kerala Jobs
- Madhya Pradesh Jobs
- Manipur Jobs
- Mizoram Jobs
- Odisha (Orissa) Jobs
- Punjab Jobs
- Sikkim Jobs
- Telangana Jobs
- Uttar Pradesh Jobs
- West Bengal Jobs